1980 (Geng Shennian) United Nations convened "United Nations new
The Energy and Renewable Energy Conference defines new energy as a basis for the modernization and utilization of traditional renewable energy based on new technologies and materials, and the replacement of resources with inexhaustible and renewed renewable energy. Fossil energy that pollutes the environment, focusing on the development of solar energy, wind energy, biomass energy, tidal energy, geothermal energy, hydrogen energy and nuclear energy (atomic energy)
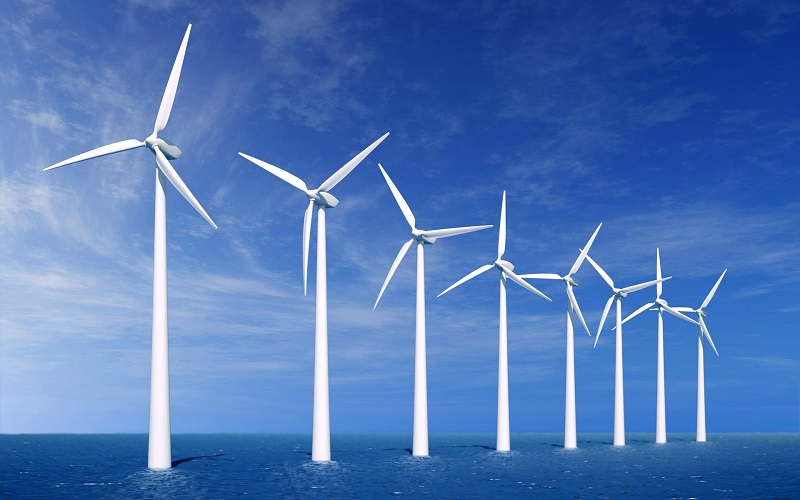
New energy generally refers to renewable energy that is developed and utilized on the basis of new technologies, including solar energy, biomass energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, wave energy, ocean current energy and tidal energy, and thermal cycling between the ocean surface and deep layers. In addition, there are hydrogen energy, biogas, alcohol, methanol, etc., and coal, oil, natural gas, water energy and other energy sources that have been widely used are called conventional energy sources. With the limited energy of conventional energy and the increasingly prominent environmental problems, new energy sources with environmental protection and renewable characteristics are receiving more and more attention from all countries.
The new energy sources that can form industries in China mainly include water energy (mainly small hydropower stations), wind energy, biomass energy, solar energy, geothermal energy, etc., and are clean energy that can be recycled. The development of new energy industry is not only an effective supplementary means for the entire energy supply system, but also an important measure for environmental governance and ecological protection, and is the ultimate energy choice to meet the sustainable development needs of human society.
Generally speaking, conventional energy refers to energy that is relatively mature in technology and has been used on a large scale. New energy usually refers to energy that has not been widely used and is being actively researched and developed. Therefore, coal, oil, natural gas, and large and medium-sized hydropower are regarded as conventional energy sources, and solar energy, wind energy, modern biomass energy, geothermal energy, ocean energy, and hydrogen energy are used as new energy sources. With the advancement of technology and the establishment of the concept of sustainable development, industrial and domestic organic waste, which has been regarded as garbage in the past, has been re-recognized and intensively researched and exploited as a material for energy resource utilization. The resource utilization of waste can also be seen as a form of new energy technology.
The energy resources that are newly developed and utilized by human beings and need further research and development are called new energy sources. Compared with conventional energy sources, new energy sources have different contents in different historical periods and technological levels. In today's society, new energy usually refers to solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, hydrogen energy and so on.
According to categories, it can be divided into: solar energy, wind energy, biomass energy, hydrogen energy, geothermal energy, ocean energy, small hydropower, chemical energy (such as ether-based fuel), nuclear energy, and so on.